Probiotics in food
and medicines



Probiotics as food and as medicine
The consumption of microorganisms dates back to ancient times. Even then, the beneficial effects of fermented food on human health were noted, although it was not yet known that bacteria and yeasts were responsible for fermentation. The use of fermented milk goes back to the distant past. This tradition is maintained, but it has progressed, which implies the improvement of fermented products by adding probiotic bacteria.
The interest in probiotics began to grow in the 1990s due to the increasing antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria, making probiotic bacteria one of the alternative antimicrobial strategies to boost immunity and reduce antibiotic use. With the usual addition of probiotic bacteria to yogurt and other fermented dairy products, probiotics are increasingly being mixed into chocolate, biscuits and energy bars made of cereal flakes, seeds and dried fruits. The consumption of probiotics in the form of capsules or water-soluble granules is also becoming more and more popular.
Probiotics
Usually lactic acid bacteria, are useful live microorganisms that we consume because of their beneficial effects on health.
Prebiotics
Non-digestible carbohydrates that serve as an energy source to the beneficial bacteria that make up the gut microbiota.

Yogurt bacteria as probiotics
How do we obtain a yogurt with a thick texture and rich sour taste from milk with a slightly sweet taste?
The answer lies in the process of lactic acid fermentation of milk, which takes place with the help of the lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus. By the action of their enzymes, the milk sugar lactose breaks down into glucose and galactose and the lactic acid is produced. There is a change in the organoleptic properties of milk. The acetaldehyde is also produced, which, along with lactic acid and other fermentation products, gives yogurt a distinctive taste and flavor that we all enjoy so much.
Other fermented milk drinks are produced in the same way, only by using other types of lactic acid bacteria. Therefore, the taste and aroma of sour or acidophilus milk and kefir are different from the taste of yogurt, even though a cow's milk is used for all these products.


 It is said that Genghis Khan and his warriors lived on yogurt. Isaac Carasso first began selling yogurt in Barcelona, Spain in 1920. He founded the company "Danone", which he named after his son. "Danone" is still today one of the largest dairy companies in the world.
It is said that Genghis Khan and his warriors lived on yogurt. Isaac Carasso first began selling yogurt in Barcelona, Spain in 1920. He founded the company "Danone", which he named after his son. "Danone" is still today one of the largest dairy companies in the world.
Why is it recommended to consume yogurt?
It is rich in nutrients and a good source of protein, vitamin D and calcium. These nutrients help build strong muscles and bones and provide energy! Live bacterial cultures in yogurt enhance lactose digestion.

Probiotics as medicines
Until the second generation of probiotics as "live biotherapeutic products” (LBPs) appears on the market, at our disposal are probiotics as food supplements. Both are encapsulated powdered probiotic products, which contain dried, but live probiotic bacteria obtained by the lyophilization (freeze-drying) process. Microencapsulation is often used for additional protection of probiotic bacteria.
Our video called Lyophilization.
The removal of water through drying represents stress for the bacterial cell. To maintain their ability to revive after rehydration, various sugars, proteins, glycerol, and other molecules that play a protective role during the drying process are added before that process.
Removal of water represents stress for the cell as the cell membrane phospholipids have to withstand the transition from liquid to the gel phase. In the cytoplasmic membrane, phospholipids are hydrated. The removal of water increases the Van der Waals forces between hydrocarbon chains, resulting in membrane damage. Adding sugar has an impact on lowering the temperature at which this transition takes place because they bind to the surface of phospholipids instead of water surface, thus preserving the structure of the cell membrane. This means that the hydrogen bonding between the phosphate group of phospholipid and the hydroxyl group of sugar is due to the protective effect of sugar.
Lyoprotectants and lyoprrotectants are additives used during freezing, drying and osmolysis, or lyophilization, whose role is to stabilize the membrane and prevent irreversible damage to cellular biopolymers. In addition to mono-, di-, and polysaccharides, other substances such as milk and whey proteins, sugars, amino acids, and their derivatives may be used as lyoprotectants. In our laboratory (Laboratory for Antibiotic, Enzyme, Probiotic and Starter Cultures Technology, Faculty of Food Technology and Biotechnology, University of Zagreb) skim milk proved to be a very good lyoprotectant, even better than sugars, which can be attributed to the additional protective effect of the present proteins and amino acids that stabilize the macromolecule structure and the bacterial cell membrane.


The oral administration is the next stress for probiotic bacteria because they need to survive passage through the stomach and small intestine, where gastric acid (low pH), digestive enzymes and bile salts represent obstacles to their survival.
What is microencapsulation?
To ensure the survival of probiotic bacteria and preserve their activity during drying as well as after passing through the digestive system after consumption, an innovative technological procedure called microencapsulation is applied. It is the process of immobilization of probiotic bacteria within a limited space of the carrier, usually a natural polymer such as alginate, whereby microcapsules, within which probiotic bacteria are protected from stressful environmental conditions, are produced. Such microcapsules are also lyophilized (freeze-dried) and placed on the market in the form of granules.

Microcapsules of probiotic bacteria
The vials contain live probiotic bacteria in the form of beads, obtained by their cross-linking into biopolymer alginate (polysaccharide from brown algae), which should protect them when passing through the stomach and small intestine, where the conditions are unfavorable for them (low pH in the stomach and of bile salts in the small intestine), and during the drying process. Thus when dried, we consume them as probiotics.


 Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus
Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus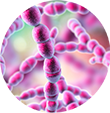 Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus
Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus




