Is there anyone
in the drinking water?


Is clean water always potable water?
Drinking water or tap water is high-quality water that is regularly analyzed and is suitable for human needs. Under the term “clean water” we often assume spring water, that is, water from some source in nature. The main difference between spring water and tap water arises from the fact that tap water is purified and, because of the added chlorine, is safe to consume.
Find out more on video file.
Source - author: youtube.com - Concerning Reality

Springwater may be potable, but it is not safe for consumption because it may also contain microorganisms that cause disease in humans.


It’s good to know:
Natural mineral or natural spring water, which is bottled at the source without further treatment, can be purchased as bottled water. That water is not chlorinated, but it is quality controlled.
What treatments must drinking water undergo to be suitable for human consumption?
The water we drink should be colorless, odorless and tasteless and must meet health safety standards . Therefore, the water drawn from surface or ground sources undergoes numerous treatments before it reaches the consumer's tap.
Depending on the quality or purity of the water in its original state, the water undergoes a complete or only partial purification process. So, for example, very pure water undergoes only the , while water that is not sufficiently pure in the natural state undergoes the entire purification process.
The drinking water treatment process begins with the removal of impurities and insoluble substances, i.e. mechanical treatment of water. Mechanical treatment includes the processes of , , deposition and .

1. Untreated water
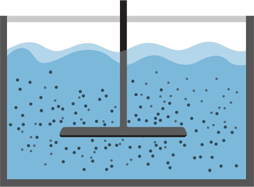
2. Coagulation

3. Flocculation
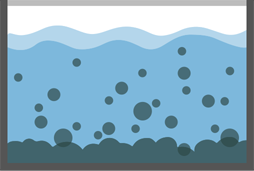
4. Sedimentation
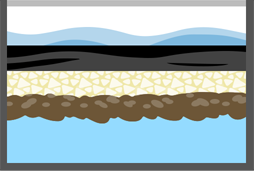
5. Filtration

6. Clean water

7. Water used in our household
The mechanical treatment is followed by the disinfection of water, which aims to destroy or inactivate potentially pathogenic bacteria. Disinfection of drinking water is the most effective measure to prevent the occurrence and spread of hydric epidemics. Water disinfection can be conducted using , , heat or . However, it is most commonly done by adding (in more than 90% of cases).
Once suspended substances and microorganisms are removed from the water, the water is safe for consumption and can be delivered to end-users.


To keep the drinking water healthy, there should be no Escherichia coli, Enterococcus species, Clostridium perfringens and enteroviruses!
How do we know that the water we consume meets health safety standards?
Control of drinking water safety for human consumption is legally required. The purpose of this control is to obtain basic information on the physical, chemical, and microbiological parameters of water and thus to verify the effectiveness of the water treatment processes mentioned earlier.
Microbiological parameters, among others things, are used to assess drinking water quality for human consumption to indicate the degree of contamination of water by microorganisms. Microbiological parameters include monitoring the presence of Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, , a bacterium of the genus Enterococcus and enteroviruses. The analysis of these indicators is carried out by determining the number of bacteria or viruses in a given volume of water.
The maximum permissible limit (MPL) of these microorganisms in water is zero, i.e. their presence in the water sample is not permissible. If it is determined that some of these microorganisms are present in the analyzed water, such water is labeled as defective and, therefore, unfit for human consumption.





Contaminated drinking water - how to identify it and what to do?
If the drinking water is discolored, contains visible impurities or has an unusual taste or an unpleasant smell, such water is unfit for consumption. In this case, it is necessary to inform the competent water supply facility and follow the instructions given.

If you have been away from the household for a long time, let the water run from the tap for at least five minutes to wash away any dirt and microorganisms from the tap.

Growth of colonies on a chromogenic medium from the first water jet after seven days of not using the tap (left Petri dish) and after the water had flowed for 5 minutes (right Petri dish).
Cohabitants in the kitchen sponge
A kitchen sponge for dishwashing is one of the dirtiest things in our household. We do the dishes with a sponge, but what's left in the sponge after that?
Bacteria are tiny microorganisms that are not visible to the naked eye. They come from food, and after washing dishes, and the kitchen sponge becomes their new home. Bacteria are happy because they live in a warm and humid place, and there is plenty of food around them.

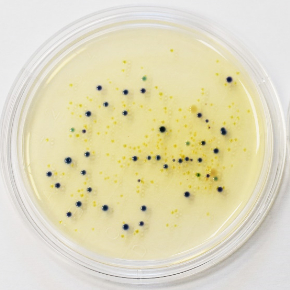
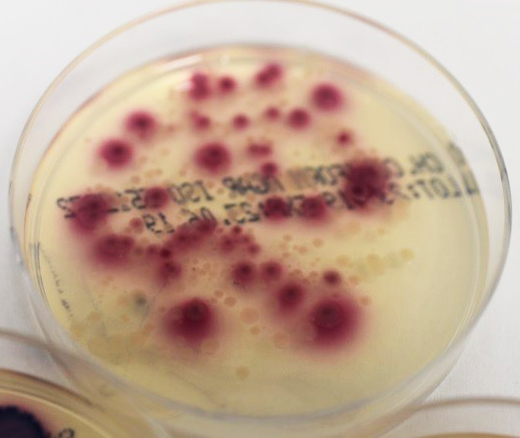
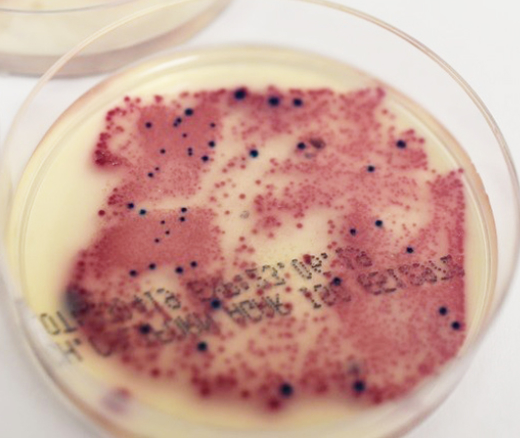
Growth of bacterial colonies on a chromogenic media for cultivating coliform bacteria from sponge samples used in the kitchen after 3, 7 and 14 days. According to the characteristic growth of colonies on a chromogenic media, we can distinguish Enterobacter aerogenes as pink-colored colonies, Escherichia coli as blue colored colonies and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as transparent colonies.
1 - 3 days of use
2- 7 days of use
3- 14 days of use
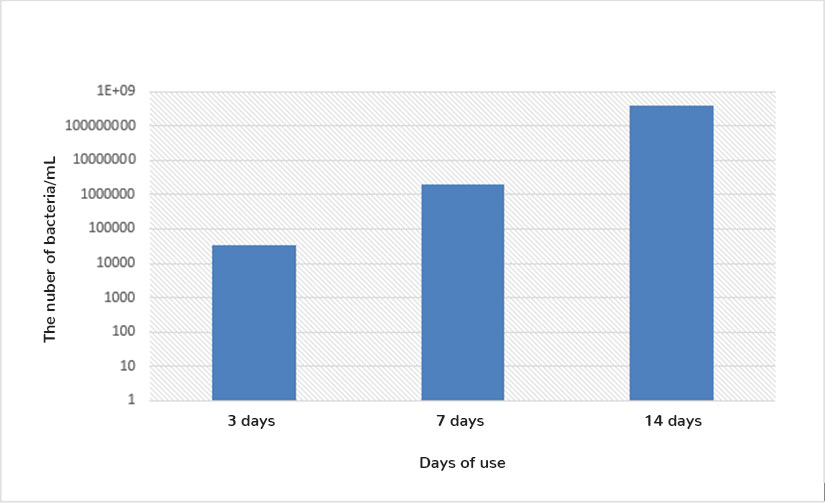
The number of bacteria isolated from sponge samples used in the kitchen for 3, 7 and 14 days.