Gastrointestinal system -
Home of probiotic bacteria

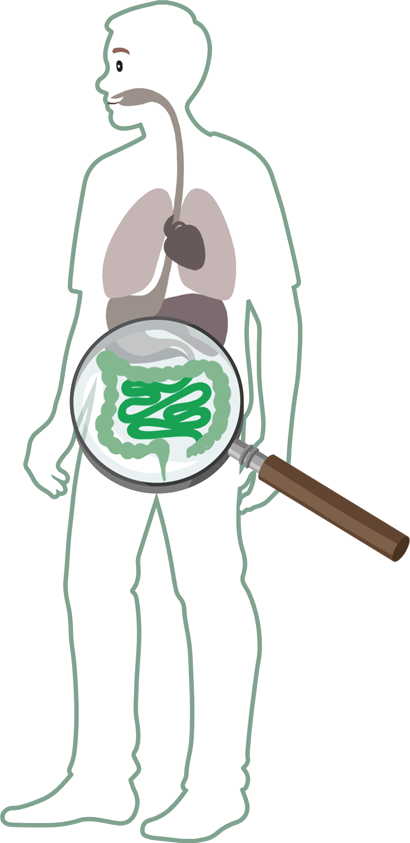
Human gut microbiota
We acquire many of our „good“ bacteria at birth. The intestinal microbiota of the infant develops under the influence of the maternal microbiota at birth, except in the case of a caesarean section when the microbiota from the maternal skin influences the infant. Children who were breast-fed have better immunity and better intestinal microbiota in comparison to formula-fed children.
The human digestive system contains more than 1000 different types of bacteria that help maintain a healthy digestive and immune system.
What are these bacteria?
The bacteria of the gut microbiota that produce short-chain fatty acids (acetic, propionic and butyric) are considered to be particularly useful. This is because the absorption of these acids in the gut contributes to increasing the body's energy levels, aids metabolic processes, affects the storage of fat and maintains the function of the intestinal mucosa.
Microbiota
All microorganisms present both in and on the surfaces of the human body, or in or on some part of the body.


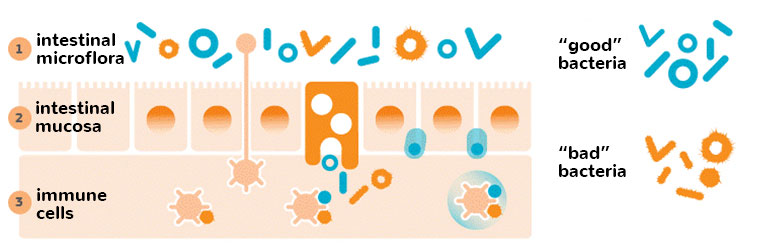
The bacteria in the gut protect the person from pathogenic infection and, more importantly, boost the immune system. A presence of the good bacteria makes it difficult for pathogens to survive because of the production of organic acids (primarily lactic and acetic acids), which inhibit the growth and multiplication of pathogenic bacteria.
According to recent research, a balanced composition of the gut microbiota is an important factor in maintaining body mass, protecting the body from allergies and preserving mental health. In contrast, an imbalanced gut microbiota composition may also be one of the causes of depression.
Finf out more about microbiota
A diet rich in vegetables, fruits and whole grains leads to a balanced gut microbiota composition.
Dysbiosis
A balanced gut microbiota, which contains about 85% of "beneficial" bacteria and 15% of "harmful", is essential for health and vitality. The condition in which this ratio is disrupted is called dysbiosis. Dysbiosis occurs when there are too many types of bacteria in the digestive system that have a negative effect, and too few of “beneficial bacteria”.
Find out about good and bad bacteria

Good bacteria



Bad bacteria



Lactobacillus

An example of the antimicrobial activity of probiotic bacteria against pathogenic bacteria:

In the joint cultivation of probiotic and pathogenic bacteria, the number of living cells of the pathogenic bacterium is gradually reduced due to the inhibitory effect of the probiotic bacteria in which presence the pathogenic bacteria cannot grow. The first Petri dish in the figure (from left) shows the increased number of colonies of the pathogenic bacteria before adding the probiotic bacteria to the sample, and the second and third Petri dishes show how the number of pathogenic bacteria decreases over time.
Link to work of our laboratory.


Digestive system - keeper of the immunity
Due to improper diet, stress, use of medicines, especially antibiotics, and unhealthy habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, the balance of the gut microbiota is often disrupted. Various diseases, fever and diarrhea can disrupt the gut microbiota, but also vice versa - altered gut microbiota composition can cause many health problems, from diarrhea to autoimmune diseases and obesity.
The use of probiotics, as a help to treat digestive diseases, was preceded by intensive research in the second half of the twentieth century. These bacteria and their enzymes inhibit the growth of pathogens, thereby maintaining the balance of the gut microbiota.


Did you know that even 70% of our immune system cells are in the gut and that they recognize and destroy substances that could be harmful to the body?
It is interesting and important to note that probiotics have a beneficial effect on athletes. According to some studies, strenuous trainings can lead to "silent" inflammation of the intestine, which are manifested by digestive disorders such as diarrhea and constipation. Disrupted balance of the intestinal microbiota is not only a possible threat to the development of disease states, but can also negatively affect the metabolism of macro- and micronutrients.
Conclusion:
It is not necessary to consume probiotics when we are healthy.
However, they will help a lot with the digestive problems that can be caused, for example, by antibiotic therapy that can disrupt the gut microbiota composition. So far, scientific research suggests that probiotics can help restore the balance of the gut microbiota by competing for binding sites and nutrients in the gut. They help in the production of organic acids, which suppress pathogens and undesirable bacterial species in the gut, and thus maintain and improve immune and gastrointestinal function.

 Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus
Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus Bifidobaterium spp.
Bifidobaterium spp. Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus
Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus Salmonella spp.
Salmonella spp. Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori

