Diseases caused by fungi



Can fungi affect us?
Yes, they can.
Some fungi can contain poisons, so our health, even life, can be endangered if we eat them. The poisonous fungi are large and grow mostly in forests or fields. Besides them, there are also tiny microscopic fungi. These fungi can cause diseases in humans and animals. They belong to a large group of living organisms we call eukaryotes.
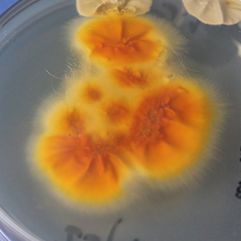
Some fungal species are similar to each other and based on this they are classified into groups. A large group is consisted of molds, type of fungi that are more complex in structure.
Some types of molds are divided into separate groups of similar shapes and lifestyles. Within the mold group, are molds called dermatophytes, and the diseases they cause in humans and animals are called dermatophytoses.


Dermatophytes are widespread in nature, in the ground, in animals and in humans.
Geophilic dermatophytes
The ones we find in the soil
Anthropophilic dermatophytes
Dermatophytes whose the main host is human.
Zoophilic dermatophytes
Dermatophytes whose the most common host are animals.

Soil is a natural habitat for geophilic dermatophytes
However, when an animal or human comes into contact with the soil in which the dermatophyte (e.g. Microsporum gypseum) is present in the form of a spores (parasitic form), the dermatophyte can adapt to the skin or hair conditions of the new host, thereby infecting the human or animal. In dogs, usual sites of the infection are the muzzle or front paws that the dog uses for digging in the ground, and in humans, these sites are most commonly hands after soil tillage.



Different types of animals are the natural hosts of zoophilic dermatophytes.
They are mostly transmitted by direct contact among certain animals. Also, people can get infected through direct contact with infected animals. Usually, this implies kids who may become infected after playing with stray cats. Such infections are much more common in urban areas due to the large number of stray cats. Also, healthy animals can evidently carry and transmit a pathogen to other animals and humans, so they represent a possible source of infection.



Caution!
In humans, zoophilic dermatophytes, such as Microsporum canis, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton verrucosum cause more pronounced inflammatory changes on infected areas of the skin, very often of a characteristically recognizable form. However, animals can also become infected amongst each other. It happens especially in large-scale livestock production or on occasions when the animals live in confined spaces, so they are in close contact.

Anthropophilic dermatophytes are almost regularly the cause of dermatophytosis in humans who are their natural host. Transmission to animals is rare, although this possibility is not excluded.


A group of dermatophytes consists of several dozen different species. Here we are going to mention only those that most commonly occur in animals such as pets - cats, dogs, guinea pigs and others. Namely, some of these animals (such as stray animals or animals kept in a large number in common animal accommodations), because of the way of life, may more easily come into contact with these fungi and then become infected.
Find out more in video file.
Source - author: youtube.com - American Veterinarian
There are many diseases caused by dermatophytes in humans and animals. To get basic information about these diseases, we will meet some of these dermatophytoses - microsporosis and trichophytosis.
Microsporosis is most common in cats and dogs but it can be transmitted to humans via contact, and trichophytosis is a disease transmitted to humans via contact with fur-bearing animals such as guinea pigs, rabbits and hamsters.