Fruits and vegetables strike back
Fruits and vegetables are an excellent substrate for the growth of bacteria, yeasts and molds. Find out why!
Microorganisms have a warlike tactic of attacking fruits and vegetables - they attack from the surface and slowly penetrate the rest of the tissue.
They are characterized by a high proportion of water, which is very important for our body. However, this is suitable for other organisms, even for those we do not see with the naked eye. The more mature foods are, the more attractive they are to microorganisms because the fruit is more mature, contains more sugar and is a better base for growth and development. The number of microorganisms increases over time, causing huge losses of fruits and vegetables intended for human consumption worldwide.



There are so many types of apples, that it would take you 19 years to try each without eating one type twice.
The fruit is acidic because it has a lower pH value, which is suitable for the growth and propagation of yeasts and molds. Constant attacks of bacteria soften the tissue and cause various changes in color and texture.
In fruits, the pH value is usually below the limit suitable for bacterial development, so bacteria are not present in the initial stage of fruit spoilage, unlike yeasts and molds that tolerate well the acidic environments.

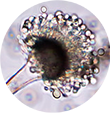
Penicillium
The mold of the genus Penicillium is an example of a green-colored mold. The biggest opponent was Penicillium expansum which engulfs mechanically damaged fruits, most commonly citrus and apple fruits. Namely, due to the damaged peel, the entrance of the microorganism is facilitated.
Alternaria tenius
It appears in the form of a green-brown color, and also causes black spots.

Aspergillus niger
A black mold that attackes fruits, and especially peaches, grapes and plums.

Botrytis cinerea
Strawberries, cherries, grapes, along with some other fruits, can do little to counteract the greyness caused by Botrytis cinerea.

Vegetables are less acidic and grow from the ground, which is why they are in close contact with microorganisms.
The bacteria attack the already damaged vegetables, softening them and creating unpleasant smells and causing spoilage. Certain bacteria show their presence in a specific way. Some are manifested by watery rot in potatoes or cottony rot in carrots.
In addition to the molds mentioned earlier, are the molds and which like vegetables and are common in vegetables. If you eat vegetables contaminated with these molds, it may cause an allergic reaction and difficulty in breathing. Some molds produce mycotoxins that are toxic to our body.
Did you know?
To protect ourselves and the foods from these repulsive and harmful phenomena, some of the following things must be kept in mind. First and foremost, it is important to wash fruits and vegetables before consumption to wash away the pesticides and the various chemicals used to destroy the mold. Always pick ripe fruits because if the fruits are picked at the right time, they are of better quality and can be stored for a longer period and they should be separated from damaged or bruised ones. Also, remove already moldy fruits immediately and separate them from healthy ones, since microorganisms can easily move to other fruits.


It is recommended to preserve fruits and vegetables, which increases its durability.