Microbes -
antibiotic factories

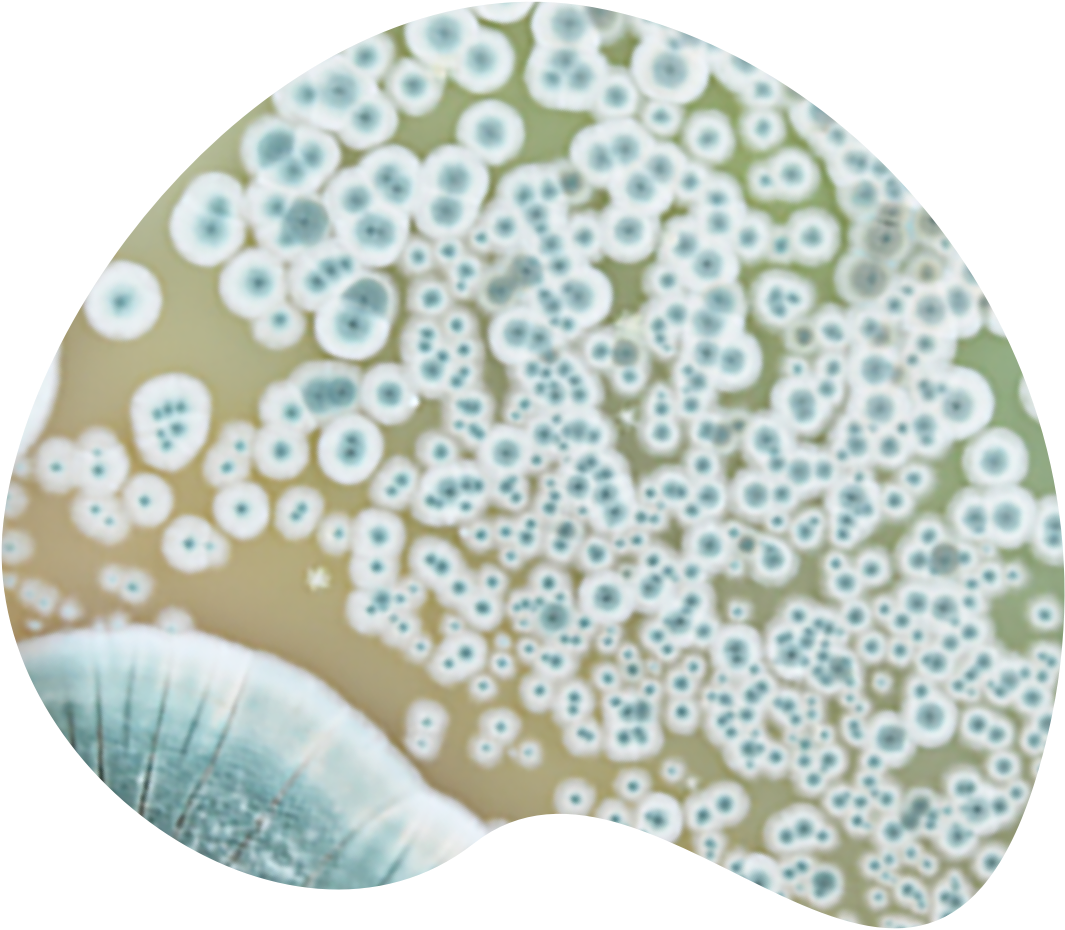

Antibiotics are…
...medicines that kill bacteria or prevent their growth and multiplication. They are used to prevent and treat infections. The name comes from the Latin words anti, meaning against, and bios, meaning life. Therefore, an antibiotic is a substance that works against life - the life of bacteria.
The discovery of the first antibiotic, penicillin, is one of the most important discoveries in history. Thanks to antibiotics, once deadly bacterial diseases have become rare and easily curable!

Have you ever wondered who “invented” antibiotics?
Where do these pills that cure us of many diseases come from? You might think that the creators of antibiotics were wise scientists? Antibiotics existed on Earth long before humans. Antibiotics are created and secreted by microbes as a weapon in the fight against other microbes with which they compete for space and food. This is a fortunate circumstance for humans who will only discover antibiotics in the 20th century and begin to use them to treat previously deadly diseases.

What would the world look like without antibiotics?
The estimated life expectancy would be fifty years, and the infectious diseases would again be the main cause of mortality.
Angel’s Glow of wounds... and what does this have to do with antibiotics ...
During the American Civil War, the wounds of some soldiers turned blue, and doctors noticed that soldiers with such wounds were more likely to survive. That is why the glow of their wounds was called Angel’s Glow. Today, it is known that wound staining comes from the bacteria .This interesting bacteria lives as a in the digestive tract of soil nematodes. It has a bluish color and produces antibiotics. Some wounded soldiers in the muddy trenches were fortunate. Their wounds came in contact with the soil and so with the nematodes and the bacteria Photorhabdus luminescens. The bacterial cells stained their wounds, and more importantly, the antibiotics they produced destroyed the and thus prevented the infection of the wounded soldiers.

How do antibiotics work?
What makes antibiotics so destructive for bacteria?
Examine the bacterial cell and learn how antibiotics work.


Which part of the cell is attacked by antibiotics?
DNA molecule
DNA - the basic molecule responsible for transmitting hereditary information in humans, bacteria and other organisms!
What do antibiotics do?
They break down DNA or prevent its replication. In this way, they prevent the transfer of information from the DNA molecule to the rest of the cell. This condition leads to the death of the bacterial cell.
An example of an antibiotic and its microbial producer:
, an antibiotic produced by .
From the golden era of antibiotics to the global crisis
One look at the color gradation is enough to realize that the era of new antibiotics discovery is behind us. The timeline takes you on a journey through the antibiotic era - past, present and future.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Number of newly discovered antibiotic groups
1920 - 1940
1940 - 1950
1950 - 1960
1960 - 1970
1970 - 1980
1980 - 1990
1990 - 2000
2000 - 2010
2010 - 2050
2050 >>


Although penicillin was discovered in 1928, humans had used antibiotics long before! It has been reported that ancient Egyptians practiced putting moldy bread on infected wounds. Thus, they were suppressing the development of harmful bacteria by the antibiotics that were secreted by the mold.